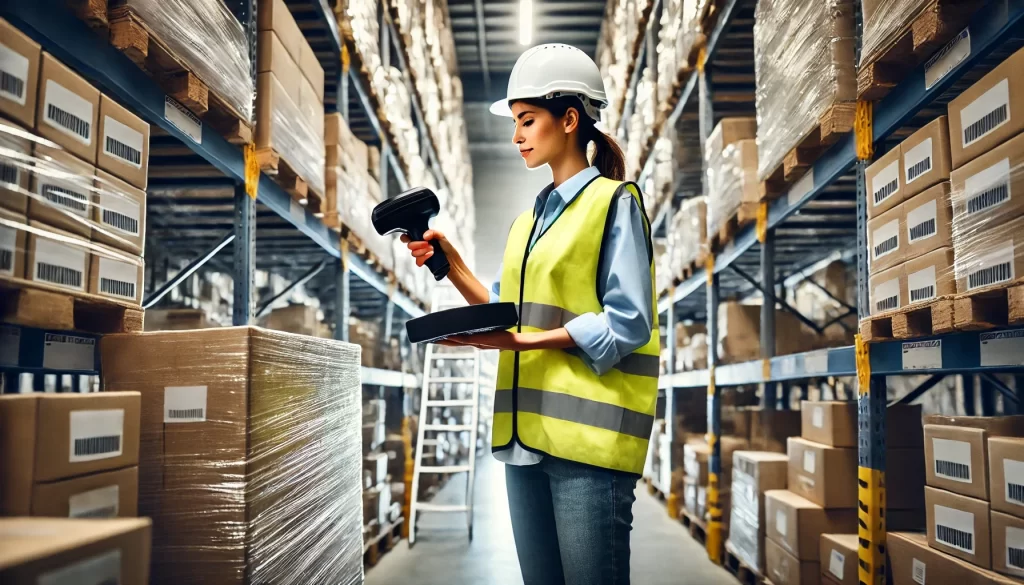
RFID technology has been around for years, and while many people know it as a convenient way to scan items in bulk from a distance, its capabilities go far beyond that. Did you know that RFID can completely automate your warehouse operations? From receiving to delivery, RFID systems can streamline the entire process. With static RFID scanners installed in your warehouse, you can constantly track your inventory in real-time. This means you’ll always know exactly where everything is, reducing errors and increasing efficiency. Imagine a warehouse where items are automatically logged as they move in and out—no more manual scans or misplaced items. RFID makes this possible, turning your warehouse into a highly efficient, automated environment.
What is RFID?
RFID, or Radio Frequency Identification, is a nifty technology that’s changing the way we manage and track items. Imagine having a magical ability to instantly know where every item in your warehouse is, without having to manually scan each one. That’s the power of RFID!
How Does RFID Work?
Here’s a simple breakdown:
- Tags: These are small devices you attach to items. They contain a tiny chip and an antenna.
- Readers: These are devices that send out radio waves and receive signals back from the tags.
- Antenna: Both tags and readers have antennas that communicate with each other.
When a reader sends out a signal, any RFID tags in the area respond with their unique information. This allows you to track multiple items simultaneously and from a distance.
Key Benefits of RFID in Warehouses
- Real-Time Inventory Management: RFID enables real-time tracking of inventory, reducing errors and discrepancies. As items move through the warehouse, RFID readers update the inventory management system instantaneously, ensuring accurate stock levels and locations.
- Enhanced Efficiency: By automating the scanning process, RFID eliminates the need for manual barcode scanning, speeding up operations and reducing labor costs. This automation allows for faster check-ins and check-outs of items, optimizing workflow and minimizing delays
- Improved Accuracy: RFID reduces human error associated with manual scanning. Items are automatically logged as they pass through RFID readers, ensuring precise inventory records and reducing the likelihood of misplaced goods.
- Operational Visibility: RFID provides comprehensive visibility into warehouse operations, including tracking the movement of goods, monitoring worker efficiency, and ensuring compliance with safety protocols. This visibility helps managers make informed decisions and quickly address issues.
- Scalability: RFID systems are highly scalable, making them suitable for warehouses of all sizes. Whether applied to individual items or entire pallets, RFID can adapt to varying operational needs, supporting growth and expansion efforts.
After considering the numerous benefits of RFID, are you still inclined to rely on traditional methods like visual inspection or handheld scanners? These older methods are more prone to human error, inefficiency, and take much longer compared to RFID. While RFID offers significant advantages in speed and accuracy, it does have some constraints and may not be suitable for all products.
Constraint of the RFID Technology
Cost:
- Initial Investment: The cost of RFID tags, readers, and the necessary infrastructure can be significant. This includes the expense of integrating RFID with existing systems and training staff.
- Tag Prices: Although prices have decreased, RFID tags are still more expensive than barcodes, particularly for high-frequency or specialized tags.
Interference:
- Materials: Metals and liquids can interfere with RFID signals, making it challenging to read tags attached to such items. Special tags or configurations may be required to mitigate these issues.
- Environmental Factors: External electromagnetic interference from machinery or other electronic devices can affect the reliability of RFID systems.
Range and Readability:
- Distance Limitations: Passive RFID tags have a limited read range compared to active tags, which can transmit data over longer distances but are more costly due to their built-in power source.
- Orientation: The orientation of the tag relative to the reader can affect readability, necessitating careful placement and alignment.
Data Security and Privacy:
- Unauthorized Reading: There is a risk of unauthorized access to RFID tag data, which can pose security and privacy concerns. Measures such as encryption and secure communication protocols are necessary to protect sensitive information.
- Data Overload: Managing and processing the large amounts of data generated by RFID systems can be challenging without robust data management and analytics solutions.
Compatibility and Standardization:
- Standards: There are multiple RFID standards and frequencies (e.g., LF, HF, UHF), and ensuring compatibility between different systems and devices can be complex.
- Integration: Integrating RFID systems with existing enterprise resource planning (ERP) and warehouse management systems (WMS) can be complicated and require significant customization.
Physical Constraints:
- Tag Durability: In harsh environments, tags may be subjected to extreme temperatures, moisture, or physical damage, requiring the use of more rugged and expensive tags.
- Size and Form Factor: For some small or delicate items, attaching an RFID tag may be impractical or aesthetically undesirable.
Worried About RFID Constraints? Here’s Your Solution!
RFID technology comes with some challenges, but there are ways to overcome them and maximize its benefits. Here are approachable solutions to common RFID constraints:
Cost Management:
- Start Small: Begin with a pilot program to test RFID on a smaller scale before a full rollout.
- Focus on High-Value Items: Use RFID for high-value or high-turnover items where the benefits outweigh the costs.
- Seek Volume Discounts: Purchase RFID tags and equipment in bulk to reduce per-unit costs.
Examples:
- Affordable Readers and Programs: You can purchase RFID readers and software programs at a much lower cost to get started. These entry-level options provide the basic functionality needed to test the technology without a significant investment, typically costing less than $1,000.
- Simple Scanners: Begin with less sophisticated, budget-friendly scanners to experience how RFID can enhance your operations. These basic models, which cost less than $500, can still provide valuable insights and demonstrate the benefits of RFID technology.
Interference Issues:
- Specialized Tags: Use RFID tags designed for metal and liquid environments to minimize interference.
- Environmental Adjustments: Position readers and antennas to avoid interference from other electronic devices.
Read Range and Orientation:
- Active Tags: For longer read ranges, consider using active RFID tags that have their own power source.
- Optimized Placement: Carefully place tags and readers to ensure optimal orientation and maximize readability.
Data Security:
- Encryption: Use encrypted RFID tags to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access.
- Secure Networks: Implement secure communication protocols to safeguard data transmitted between tags and readers.
Compatibility and Integration:
- Standardized Solutions: Choose RFID systems that comply with industry standards to ensure compatibility with other systems.
- Professional Integration: Work with experienced RFID integrators to smoothly incorporate the technology into your existing systems.
Physical Constraints:
- Durable Tags: Select rugged tags designed to withstand harsh environments.
- Innovative Tagging: Explore various tag sizes and form factors to find the best fit for your items.
RFID Trends for 2024
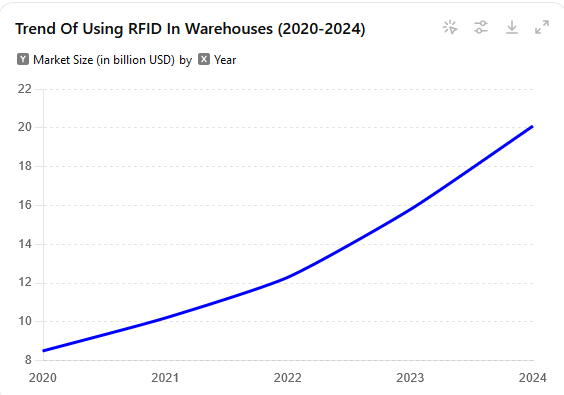
The adoption of RFID in warehouses is expected to grow significantly in 2024. As companies seek to modernize their operations, RFID is poised to become a cornerstone of warehouse automation strategies. Key trends include the integration of RFID with other advanced technologies such as autonomous mobile robots (AMRs), AI-driven analytics, and 5G connectivity to further enhance efficiency and real-time data processing.
Automate Your Warehouse with RFID Integration
Are you ready to take your warehouse operations to the next level after you determine the RFID suitable for your company? Integrating RFID with your Warehouse Management System (WMS) can streamline your processes and give you a significant advantage. Here’s how you can do it:
Choose the Right Vendor: Many vendors offer comprehensive RFID solutions tailored to various industries. Partnering with the right vendor can provide you with the tools and support you need to implement RFID technology effectively. They can offer pre-configured software and hardware solutions, along with expert guidance to ensure smooth integration.
Integrate RFID with Your WMS: To fully leverage RFID technology, you need to integrate it with your existing WMS. This integration allows real-time monitoring and automation of inventory management tasks.
Fixed RFID Scanners: Install fixed RFID scanners throughout your warehouse. These scanners continuously monitor your inventory, providing real-time data on item locations and movements.
Automate Goods Receipt and Transactions:
Receiving: When new stock arrives, the fixed RFID scanners automatically detect the incoming items. Program your WMS to perform automatic goods receipt and bin-to-bin transactions. This ensures that your inventory records are updated instantly and accurately without manual input.
Deliveries: Place RFID scanners at your dock doors to monitor outgoing shipments. As items pass through the scanner, the system automatically performs goods issues, updating your inventory and ensuring accurate records of what leaves your warehouse.
Simplify the Process with Pre-Built Programs: Implementing this level of automation might seem challenging, especially since it involves significant programming and customization of your WMS. However, you don’t have to start from scratch. There are pre-built programs and solutions available on the market that can help you achieve your goals. These solutions are designed to integrate seamlessly with your existing systems, saving you time and effort.
Conclusion
Embracing RFID technology can transform your warehouse operations, offering unparalleled efficiency, accuracy, and visibility. As the warehousing industry continues to evolve, those who adopt RFID will be well-positioned to meet the demands of the modern supply chain and stay ahead of the competition.
By investing in RFID, you’re not just improving your current operations—you’re future-proofing your warehouse for the advancements yet to come.